SOLUTIONS
Knowledge
10 Types of Drill Bits: Diagram & Application & Choose
Different Types of Drill Bits: Diagram & Application & Choose
10 Types of Drill Bits (Application and Pros & Cons)
Here are ten common types of drill bits, with a focus on overall tungsten carbide drill bits, as well as other popular drill bits:Drill Bits Type 1. Twist Drill Bit
Twist drill bits are the most common type of drill bits. They have a spiral-shaped flute design that allows for efficient chip removal during drilling. These bits are typically made from high-speed steel(HSS) or tungsten carbide, and Speed Tiger's drill bit products are made of tungsten carbide.■ Application: Twist drill bits are versatile and can be used for drilling holes in various materials such as wood, plastic, and metal. They are suitable for general-purpose drilling tasks.
■ Pros: Widely available, suitable for different materials, relatively affordable.
■ Cons: Can dull quickly when used on hard materials, may require frequent resharpening.
Drill Bits Type 2. Step Drill Bit
Step drill bits have a cone-shaped design with multiple stepped levels. Each step increases the diameter of the hole being drilled.■Application: Step drill bits are ideal for drilling holes of various sizes in thin materials like sheet metal, plastic, or PVC pipes.
■Pros: Allows for drilling multiple hole sizes with a single bit, reduces the need for multiple bits, produces smooth holes.
■Cons: Limited to thin materials, can be more expensive than regular drill bits.
Drill Bits Type 3. Masonry Drill Bit
Masonry drill bits have a carbide tip for drilling into tough materials like concrete, brick, and stone. They typically feature a fluted design to assist with debris removal.■ Application: Masonry drill bits are specifically designed for drilling into masonry surfaces and are commonly used in construction and renovation projects.
■ Pros: Excellent for hard materials, long-lasting, effective at drilling into masonry surfaces.
■ Cons: Not suitable for drilling into metal or wood, can be more expensive than regular drill bits.
Drill Bits Type 4. Spade Drill Bit:
Also known as paddle bits, have a flat, paddle-like shape with a sharp point. They are designed for drilling large-diameter holes quickly.■ Application: Spade drill bits are commonly used for drilling holes in wood, such as for running electrical wires or installing plumbing fixtures.
■ Pros: Fast drilling for large holes, suitable for wood, relatively affordable.
■ Cons: Can cause splintering in wood, not ideal for drilling into metal or other hard materials.
Drill Bits Type 5. Forstner Drill Bit
Forstner drill bits have a cylindrical shape with a center point and flat cutting edges. They create clean, flat-bottomed holes with smooth sides.■ Application: Forstner drill bits are commonly used for woodworking tasks that require precise, flat-bottomed holes, such as for cabinet hinges or dowel joints.
■ Pros: Creates clean, accurate holes with smooth sides, ideal for woodworking, suitable for drilling at an angle.
■ Cons: Not suitable for drilling deep holes, may require a drill press for optimal results.
Drill Bits Type 6. Countersink Drill Bit
Countersink drill bits have a conical shape with multiple cutting edges. They are used to create a recessed area for a screw head to sit flush with the surface.■ Application: Countersink drill bits are primarily used for woodworking and metalworking applications where screws need to be flush-mounted.
■ Pros: Creates clean, professional-looking recessed holes for screw heads, is suitable for different materials, and can be used with hand drills.
■ Cons: Limited to creating countersinks, not suitable for drilling regular holes.
Drill Bits Type 7. Auger Drill Bit:
Auger drill bits have a screw-like shape with a threaded tip. They are designed to efficiently remove wood chips during drilling.■Application: Auger drill bits are commonly used for drilling deep, clean holes in wood, particularly for tasks like installing large screws or creating holes for dowels.
■Pros: Provides fast and clean drilling in wood, ideal for deep holes, can be used with hand drills or power drills.
■Cons: Not suitable for drilling into metal or other materials, may require a steady hand to control.
Drill Bits Type 8. Brad Point Drill Bit:
Brad point drill bits have a sharp, centered point and two sharp spurs on the sides. They are designed for accurate and clean hole drilling in wood.■Application: Brad point drill bits are commonly used in woodworking tasks that require precise drilling, such as for dowels, tenons, or creating holes for joinery.
■Pros: Provides clean and accurate holes, prevents wandering or splintering, suitable for various wood types.
■Cons: Not suitable for drilling into the metal or other materials, may require frequent cleaning of wood chips during drilling.
Drill Bits Type 9. Cobalt Drill Bit:
Cobalt drill bits are made from high-speed steel (HSS) alloyed with cobalt, making them extremely hard and heat-resistant.■Application: Cobalt drill bits are used for drilling into tough materials like stainless steel, cast iron, and other alloys.
■Pros: Can withstand high drilling temperatures, excellent for drilling hard metals, long-lasting.
■Cons: More expensive than regular drill bits, not suitable for softer materials like wood or plastic.
Drill Bits Type 10. Diamond Drill Bit:
Diamond drill bits have a cylindrical shape with a diamond-encrusted tip. They are specifically designed for drilling into hard and brittle materials like glass, ceramic, or porcelain.■Application: Diamond drill bits are commonly used in tasks such as creating holes for plumbing or electrical installations in tiles, glassware, or ceramic surfaces.
■Pros: Provides precise and clean holes in hard materials, minimizes chipping or cracking, suitable for curved or irregular surfaces.
■Cons: Limited to drilling hard and brittle materials, requires water or lubrication for cooling during drilling.
Please note that the descriptions provided are general in nature and may vary depending on the specific brand or model of drill bits, and also remember to consider the specific requirements of your drilling project and choose the appropriate drill bit accordingly.
3 Steps to Find Your Right Drills Bit Easily!
And now, Speed Tiger telling you: 3 Steps to Find Your Right Drills Bit Easily!Follow these 3 steps, you will find the right drill bits easily!
- Step 1: What is your processing method?
- Step 2: What is your processing material?
- Step 3: How to choose the size you exactly need?
Parts of Drill Bit Diagram
Before that, let's take a look at what a drill should look like. There are the following parts of a drill:
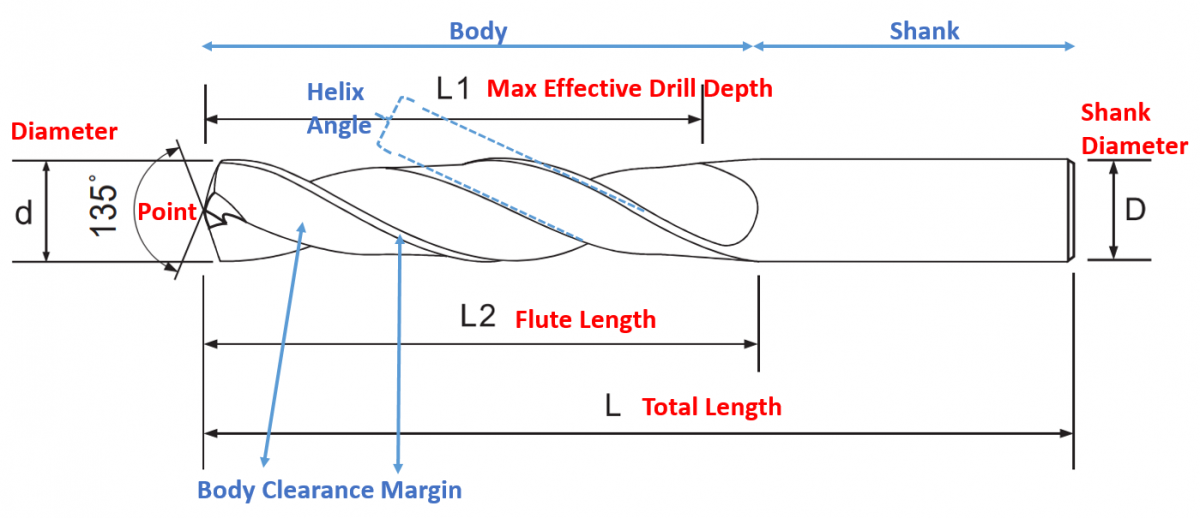
Body: The body between the shank and the point of the drill is called the body, which is fluted and relieved.
Point: The endpoint of the drill is called point and it is cone-shaped.
Different point angles are designed for different materials, this is the company's know-how.
Shank: It is the part that fits into the holding device.
Flutes: Spiral grooves on the body of the drill are called flutes, and their length is called "Flute Length"
Diameter: The diameter over the margins of a drill measured at the point.
Helix Angle: The angle is formed by the leading edge of the land with a plane containing the axis of a drill.
Margin: It's also known as a land. The length of the body across the body between the flutes. The surface of margin is part of a cylinder that is interrupted by the flutes and what is known as body clearance. This allows the drill to revolve without binding when drilling deep holes.
Body Clearance: The part of the body whose diameter is slightly less than the diameter of the drill is called body clearance, in order to reduce the friction between the drill and the walls of the hole being drilled, while the margin ensures the hole is with the accurate size.
Step 1: What is your processing method?
1) Through2) Blind
3) Flat Bottom
4) Chamfer
5) Step
6) Cross
7) Inclined Surface
Step 2: What is your processing material?
According to the specifications of ISO 513, the materials are classified into six common types according to the characteristics of the materials.| Groups | Workpiece materials | SPEED TIGER Related Products |
| P | Low-alloy steel and cast steel High-alloy steel and cast steel e.g., S45C, 1045, CK45, 1.0503; SCM440, 4140, 42CrMo4. |
PK / PKC Series FD / FDC Series |
| M | Stainless steel (austenitic) e.g., AISI 316, SUS316, 0Cr17Ni-12Mo2, SUS304, X5CrNi18-10, JIS SUS304L. |
SN / SNC Series |
| K | Grey cast iron (GCI) Ductile cast iron Nodular cast iron (NCI) |
PK / PKC Series |
| N | Non-ferrous metals: Aluminum and aluminum alloys e.g., A1070, A4032, A6061, A5052, A7075, AC, ADC, AlZnCu1.5 |
AL / ALC Series |
| S | Superalloys: - Titanium and titanium alloys e.g., Ti6Al4V, Ti6Al2Sn4Zr2Mo, Ti4Al4Mo2Sn0.5Si, Ti10Al2Fe3Al, Ti5Al5V5Mo3Cr, Ti7Al4Mo - Nickel / Inconel e.g., Inconel 601, 617, 625, Incoly 800, Monel 400, Inconel 718, 718plus, Incoly 925, Waspalloy, Hastelloy, Rene. |
SN / SNC Series for Titanium |
| H | Hardened steel e.g., SKD61, SKD11, STAVAX, SKT, HPM1, S45C, 1045, 1.0503, C45; 4140, SCM440, 42CrMo4. |
HD Series |
Step 3: How to choose the size you exactly need?
The basic 3 elements of drilling:- 1. The size of the hole
- 2. Depth of the hole
- 3. The accuracy of the hole
- The size of the hole: You use metric? Or inch? Do you know the number of tap threads? Or forming tap? Then you will know the size you need to use.
- What’s your processing depth (=Depth of the hole)?3 times of the diameter? The maximum of Speed Tiger’s Drill Bits is 8 times.
- The accuracy of the hole: There are h6 ~ h13, and the tolerance class of Speed Tiger’s Drill Bits is h7.
Drill Bit Manufacturing Tips ( Drill Bits Coating Selection)
Tips: With the correct coating on the tool, the machining effect will be multiplied with less effort!The purposes of coating are:
✔️ Increase the hardness.
✔️ Increase lubricity.
✔️ Provide better chip evacuation.
✔️ Provide a thermal barrier.
✔️ Improve the surface finish.
✔️ Reduce abrasive wear.
✔️ Prolong the tool's life.
According to the characteristics of the workpiece material and the geometry of the drill bits, we select 5 types of coatings suitable for the drills. Let's take a look at the characteristics:
| Item | Coating Type | ZrN-A | nACo | nACro | TB |
| Characteristic | Hardness (HV) | ~3400 | 45 (Gpa) | 42 (Gpa) | >6000 |
| Thickness (IJm) | 2~4 | 2~4 | 2~4 | <1 | |
| Oxidation Temp.(°C) | 900 | 1200 | 1100 | 500 | |
| Friction Coefficient | 0.3 | 0.35 | 0.35 | <0.1 | |
| Color | Golden | Blue | Gray | Black | |
| Application |
Carbon Steel | ⊚ | ⊚ | ⊚ | X |
| High Speed Steel | ⊚ | ⊚ | ⊚ | X | |
| Stainless Steel | ⊚ | ⊚ | ⊚ | X | |
| Alloy | ⊚ | ⊚ | ⊚ | X | |
| Copper / Aluminum | X | X | 〇 | ⊚ | |
| Inconel | 〇 | ⊚ | 〇 | X | |
| Titanium | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | ⊚ | |
| Plastic / Composites/ Wood / Paper |
X | X | X | ⊚ | |
| Cutting Way | Dry Cutting | ⊚ | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Wet Cutting | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | ⊚ | |
| Oil Spray | 〇 | ⊚ | ⊚ | 〇 |
Too much information?
No worries, we have already matched the drills and their coatings.
All you need to know is the material you want to process and the diameter and depth of the hole you need, and then you can choose the right drill bits from SPEED TIGER carbide drill bits series.
Related Articles:
Custom End Mill, Build a Custom Tools for your Job!
End Mill Size Standards Chart & Introduction
The Guide to Buying Carbide Drill Bits, Choose the right one for your job!
Speed Tiger is the leading Carbide End mills manufacturer in Taiwan, we provide a large range of CNC End mills, see more end mills products here.
About Speed Tiger |
Speed Tiger is a professional manufacturer of Carbide Cutting Tools and offers OEM Services, having rich experience in producing carbide cutting tools and processing consultants for more than 24 years.

Established in 1998, Speed Tiger specialized in the production of precision carbide end mills, drills, turning tools, thread mills, and other tungsten carbide steel customized cutting tools. Speed Tiger crafts cutting tools at extreme nanometer precision +-2㎛ to the exact, enabling to achieve professional cutting quality.
Visit our shop to find out more, or check out our solution to continue learning.

OTHER SOLUTIONS
-
Master Guide of CNC Milling: Process & Application Posted 2023-06-07